睾丸 Rosai-Dorfman 病
Testicular Rosai-Dorfman Disease
同义词(或曾用名): 伴有巨大淋巴结病的结外窦组织细胞增生症
发病部位: 睾丸
诊断要点:
- 罕见,多主要见于中老年男性,儿童很少发生;
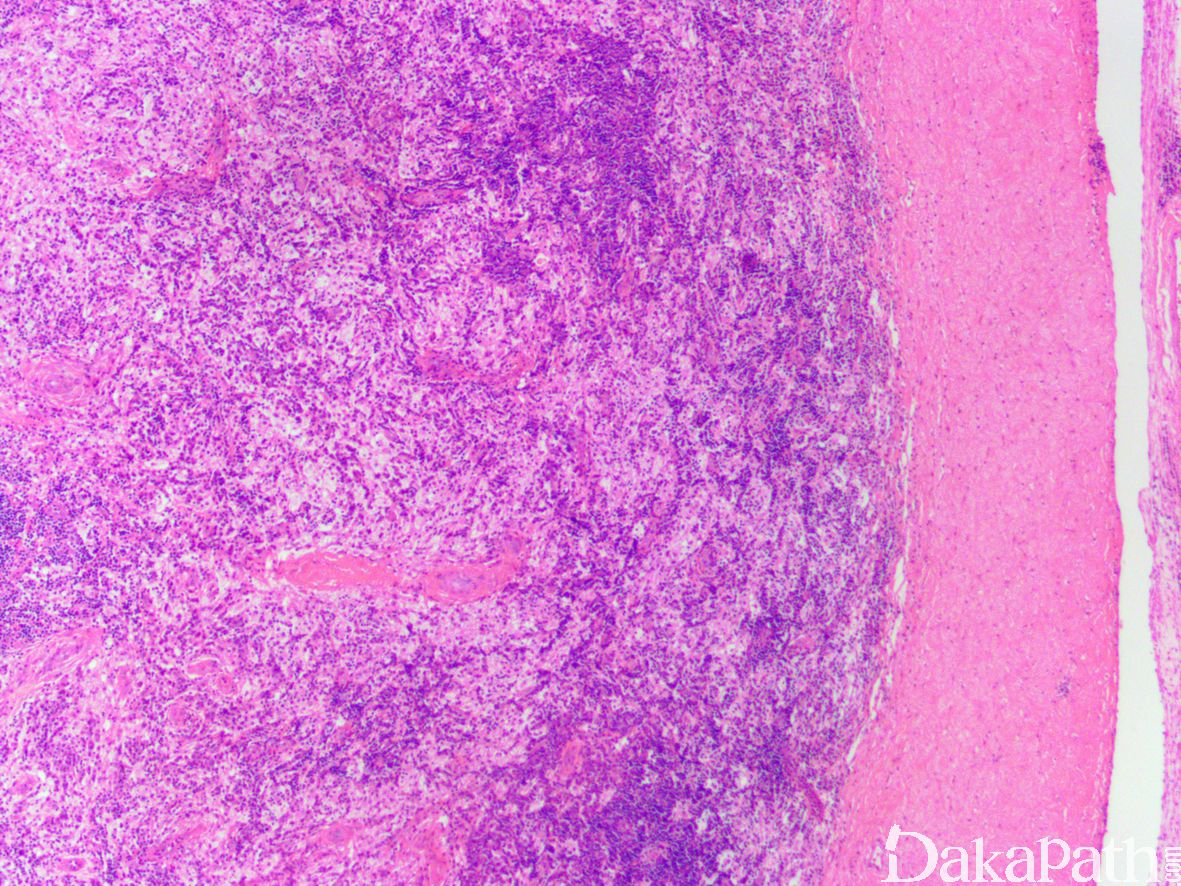
- 大体为质硬灰褐色或灰白色、黄色,部分或完全占据睾丸;可局限于睾丸,亦可发生在周围淋巴结。
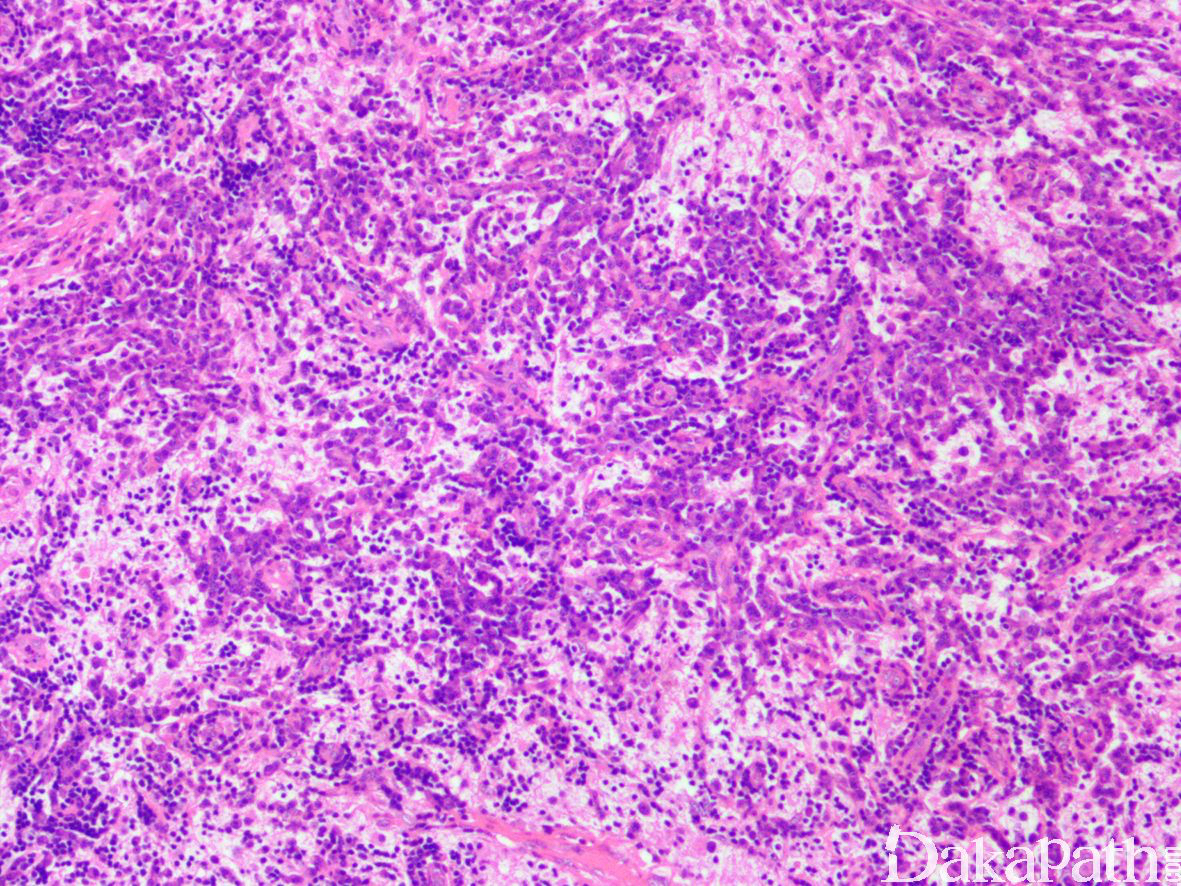
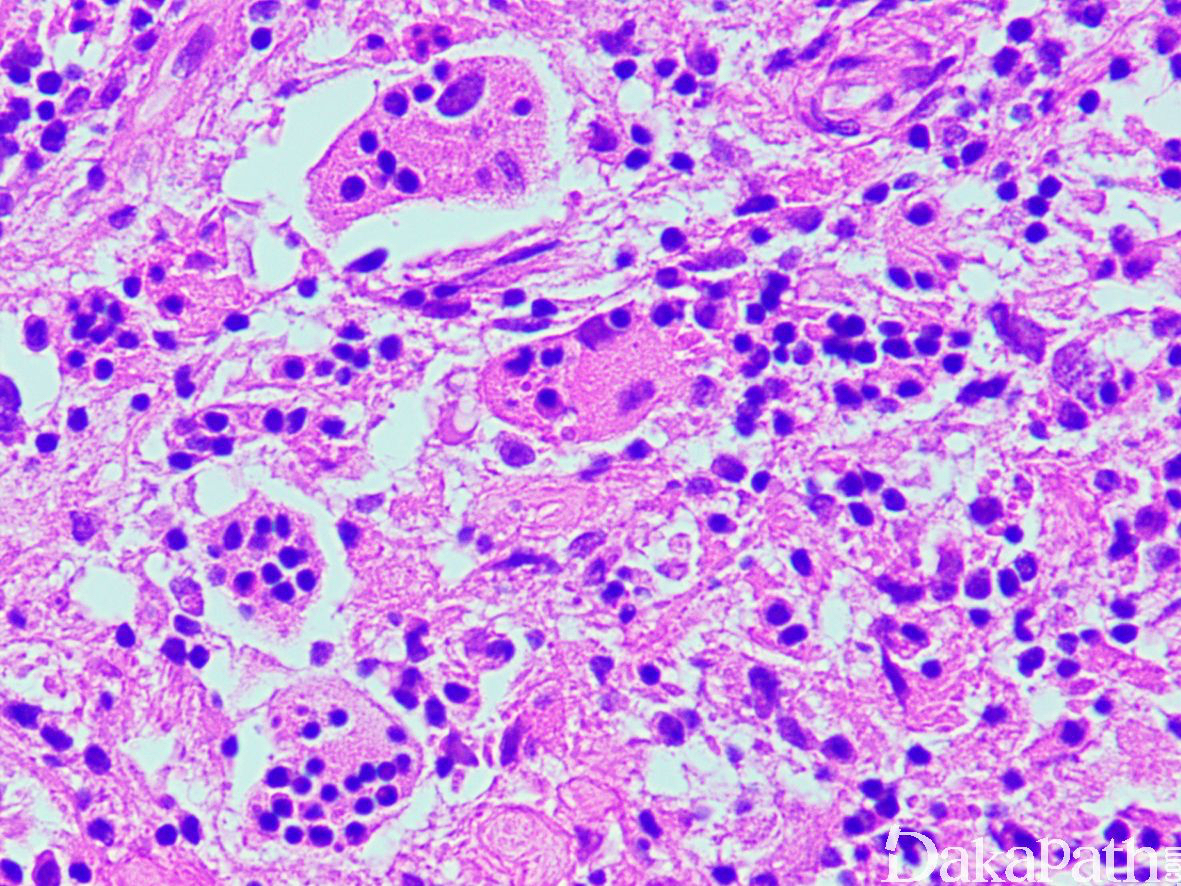
- 镜下表现为在小淋巴细胞、浆细胞、滤泡背景上可见大的组织细胞增生,细胞核大,泡状,核仁清晰,胞质丰富,呈细小泡状或颗粒状,淡染-粉染,可见淋巴细胞或白细伸入现象。
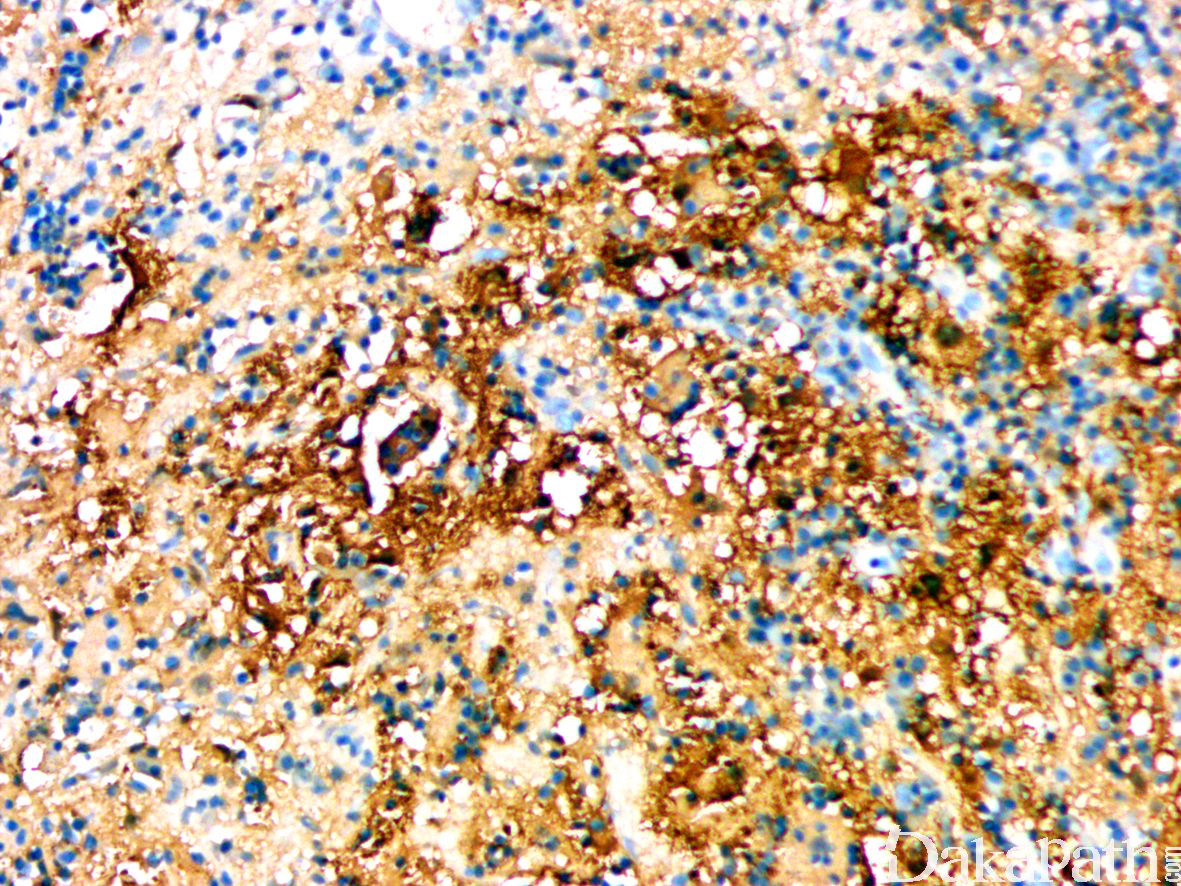

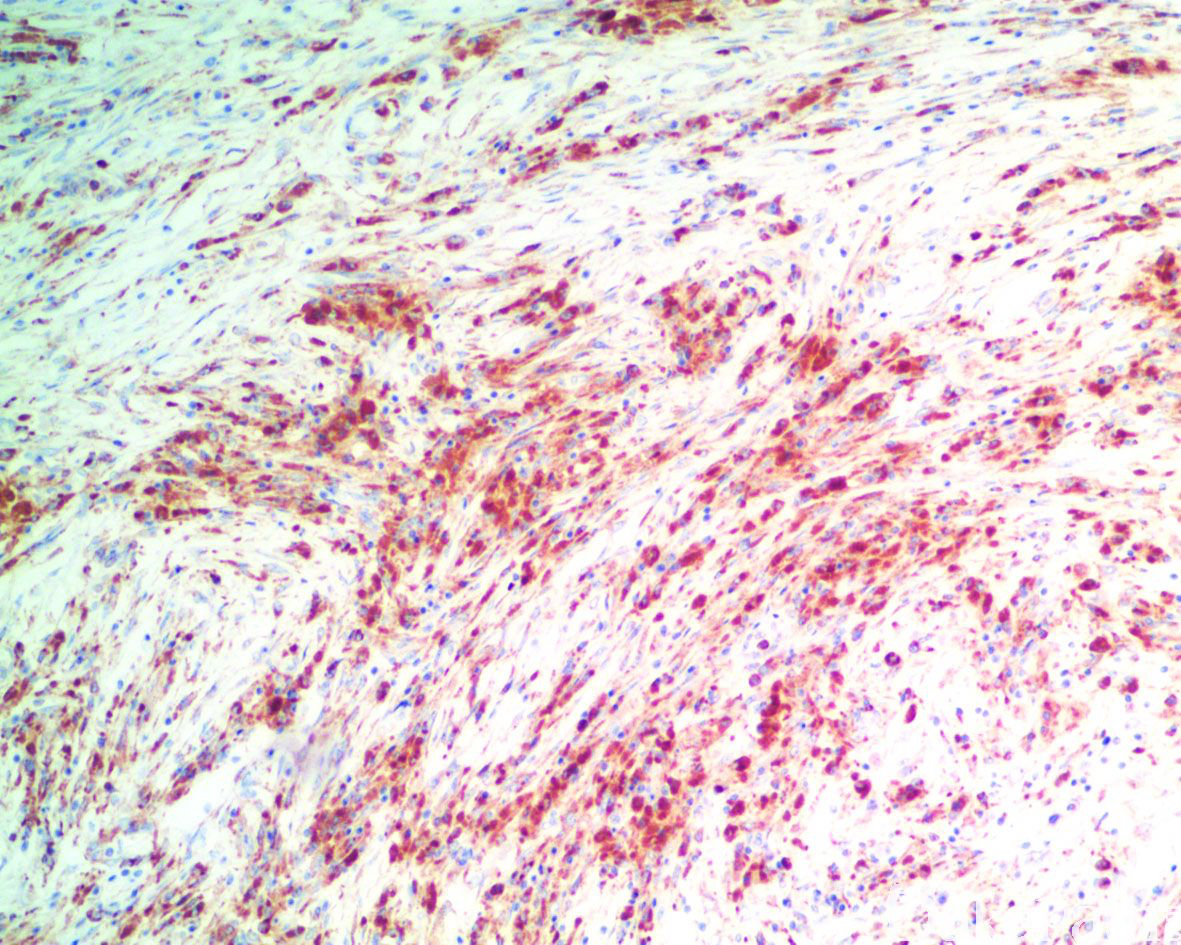
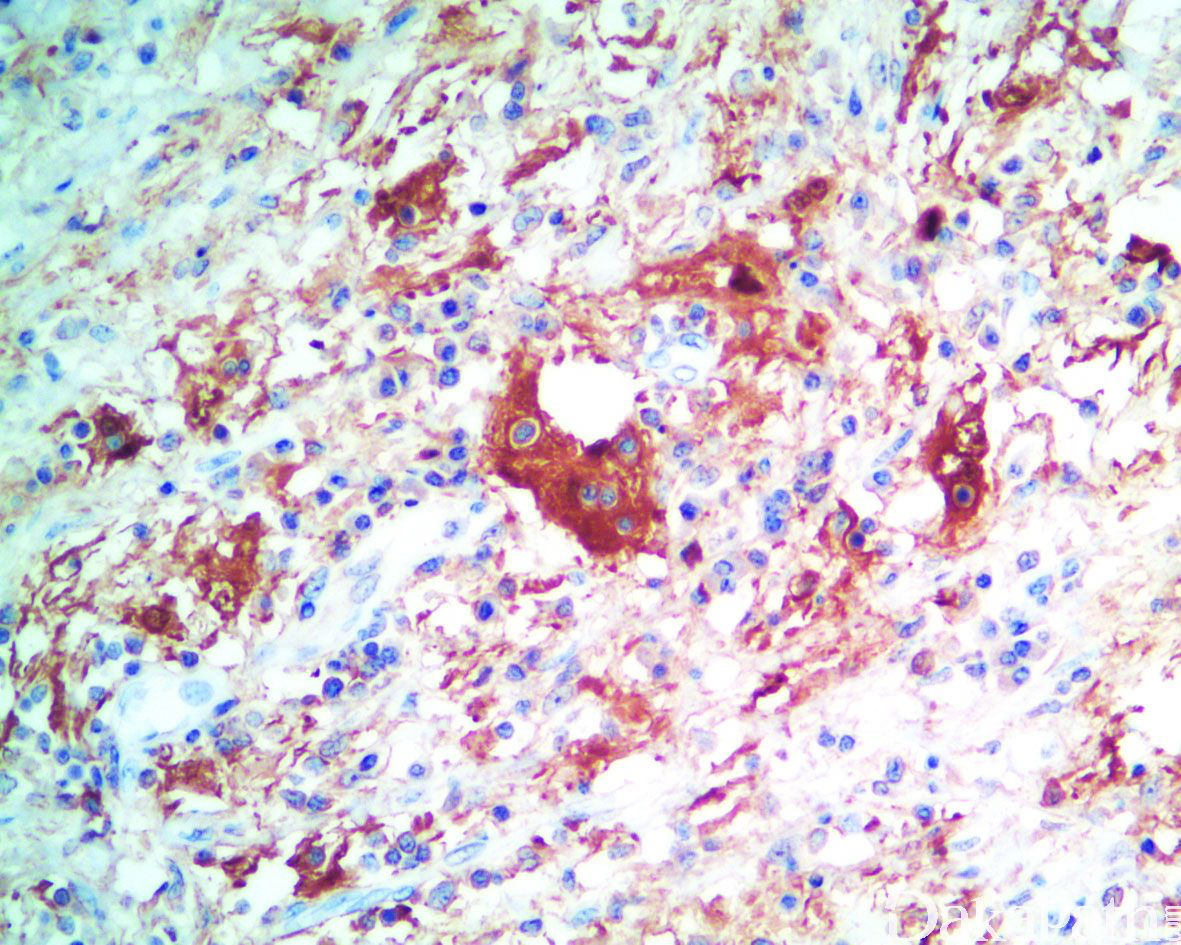
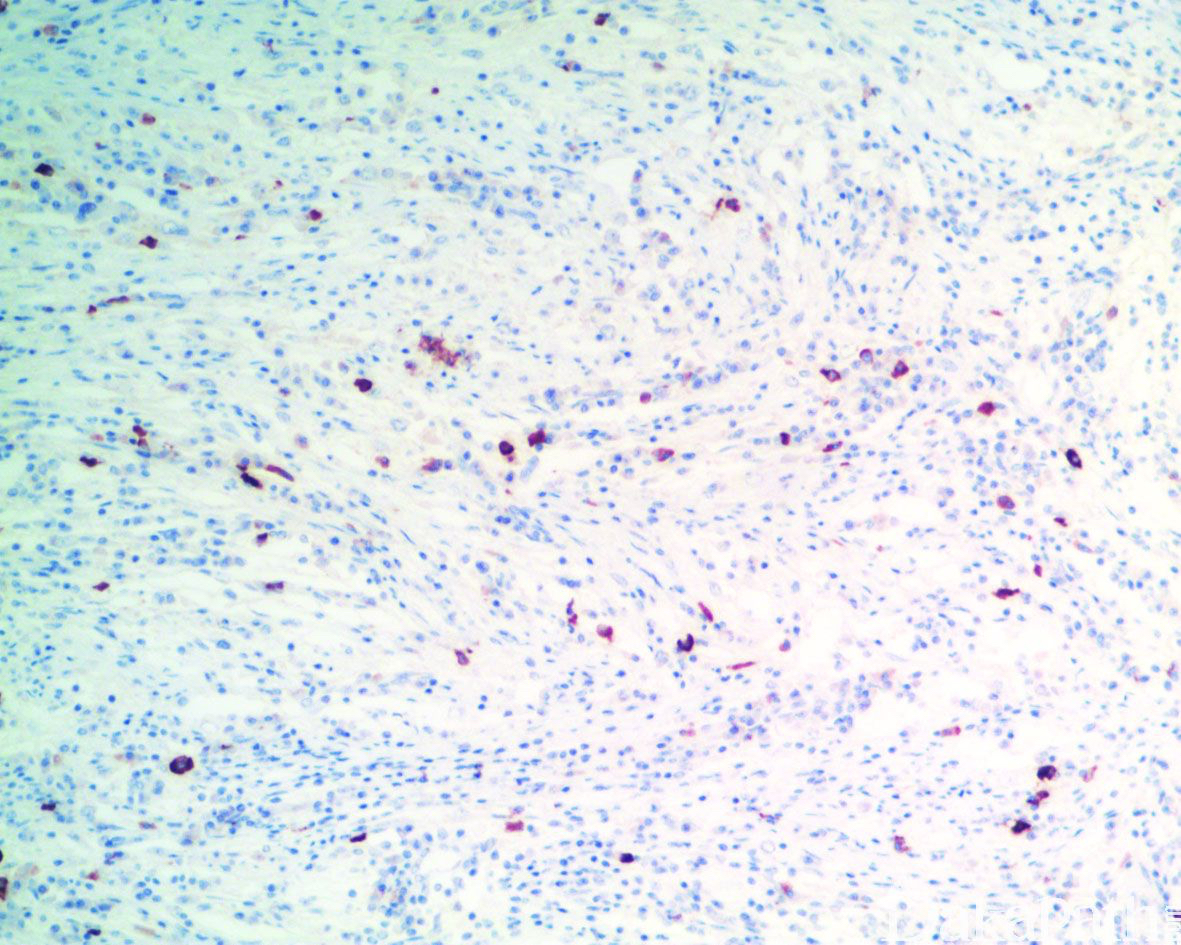
免疫组织化学染色:
组织细胞 S100 阳性,CD68 阳性,约 86%表达 cyclind1,CD1a 阴性。
鉴别诊断:
非特异性肉芽肿性睾丸炎:多型炎细胞浸润,组织细胞通常为泡沫样组织细胞,核小且核仁不明显,S100 蛋白阴性。
精原细胞瘤伴丰富的淋巴细胞浸润和肉芽肿反应:瘤细胞可见纤维性分隔,胞浆透明,核大且可见多个核仁,免疫组化染色表达 SALL4 和 OCT4 等可资鉴别。
预后:
疾病可持续存在,但一般不会进展。
治疗:
睾丸切除
病例报道:
Fernandopulle SM, Hwang JS, Kuick CH, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease of the testis: an unusual entity that mimics testicular
malignancy. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59:325–327. 参考文献:
Del G A, Moltrasio F, Young R H, et al. Involvement of the testis and related structures by Rosai-Dorfman disease: report of 2 new cases and review of the literature[J]. American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 2013, 37(12):1871. Br J Haematol. 2019 Sep;186(6):837-844. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16006. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Cyclin D1 expression and novel mutational findings in Rosai-Dorfman disease.
Baraban E1, Sadigh S1, Rosenbaum J1, Van Arnam J1, Bogusz AM1, Mehr C1, Bagg A1.
